Court Process of Family Property Disputes in Nepal
Introduction:
Disputes on family properties occurs generally when family members do not have consented division on ancestral properties. Property division should be done equally among co-parceners within a family. (Angasabanda). If you have any legal disputes related to property than choose the best property Lawyers in Nepal to solve you dispute.
Disputes related to partition/separation of family property is governed by the family law of Nepal. Legal provision relating to partition of family property are incorporated in Part-3 of Muluki Civil Code, 2074.
When and how family property separation is possible?
- Partition/division of family property can be claimed by any co-parceners anytime.
- Family property also debt (loan) is divided among co-parceners equally.
Nature of family properties that are divisible among co-parceners:
- Hereditary or ancestral property of father or grand-father. (Purkheuli sampati)
- Properties earned and increased form family’s investments (Purkheuli lagani bata badi-badayako sampati)
- Property owned and earned by husband and wife while living together.
- Common family property possessed by any family members.
What kind of properties are not divided among members of family?
- Property owned or brought by your own investment if proved.
- Insurance
- Gifts & Awards/Dowry
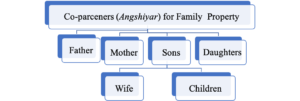
Who are Co-parceners (Angshiyar) for Family Property:
Main co-parcener are:
- Father, Mother, Sons and Daughters.
- Family property shall be equally divided among all main co-parcener.
- Partition/ divided part of husband/father’s share shall be further divided to his wife and children
Process of Family property division in Nepal:
A. Partition on mutual consent of co-parceners:
- Partition/Division balancing high and less valuable properties with consent of all coparceners.
- Partition/Division deed in written format is mandatory with prescribed legal criteria.
Note: Deed of partition should be registered in Land Revenue Office (Malpot).
B. Division of Property by court if co-parceners do not agree on mutual consent.
Court Process for Family Property Disputes in Nepal: Property Lawyers in Nepal
| S.N. | Court Process for Family Property Disputes in Nepal | Institution |
| Step 1 | File a case in district court claiming family property of your part. | District court of your jurisdiction |
| Step 2 | Submit withhold application along with inventory of family property. | Hearing on application |
| Step 3 | Order of court to withhold all disputed family properties | Order to Land Revenue office (Malpot) |
| Step 4 | Reply or defense from other co-parceners. | District Court |
| Step 5 | Examination of property inventories and witness. | Court |
| Step 6 | Final decision of the district court. | |
| Step 7 | Appeal by any party to the case | High court |
| Step 8 | Implementation of court decision | District court |
Table: Court Process for Family Property Disputes in Nepal
Disclaimer: All contains available here are for general information purposes. Proper legal solution always depends on your particular circumstances thus seek the advice from an attorney who can provide assurances of the information contained herein and interpretation of it. All liability with respect to actions taken on the basis of site’s information hereby expressly disclaimed.